Additive Manufacturing and Components Division
Also known as 3D printing, Additive Manufacturing (AM) or Fabrication is the process of joining materials to fabricate objects using data from computer-aided designs, normally through a layer-by-layer deposition process. This digital process contrast with the traditional sustractive manufacturing, where an starting complete block of a material is polished, mould nad shaped until the final piece is obtained. There are several advantages for additive manufacturing, we can highlight the flexibility and versatility in design, a decrease in energy demand, and the reduction in the time to market. The advances obtained in the last years in the field has allowed for the transition of AM from rapid prototyping to its utilisation to obtain a final productin limited series.
There are several techniques or processes available for the obtention of small pieces by AM, that can be used to obtain functional pieces in a wide spectrum of starting materials, from metalic to ceramic and polymer (plastics) materials and their mixtures. According to the ASTM Organization and its F42 standard,[1] there are seven different categories or processes to obtain a material through AM:
- Powder bed fusion
- Binder jetting
- Material extrusion
- Material jetting
- Directed energy deposition
- Sheet lamination
- Vat photopolymerisation
Each of these techniques have a series of advantages and drwbacks, and therefore each is recommended for a specific set of materials or applications. The most relevant applications nowadays for AM belong to the following sectors: aerospace and defense, automotive, electronics, construction, energy and biomedical sector.
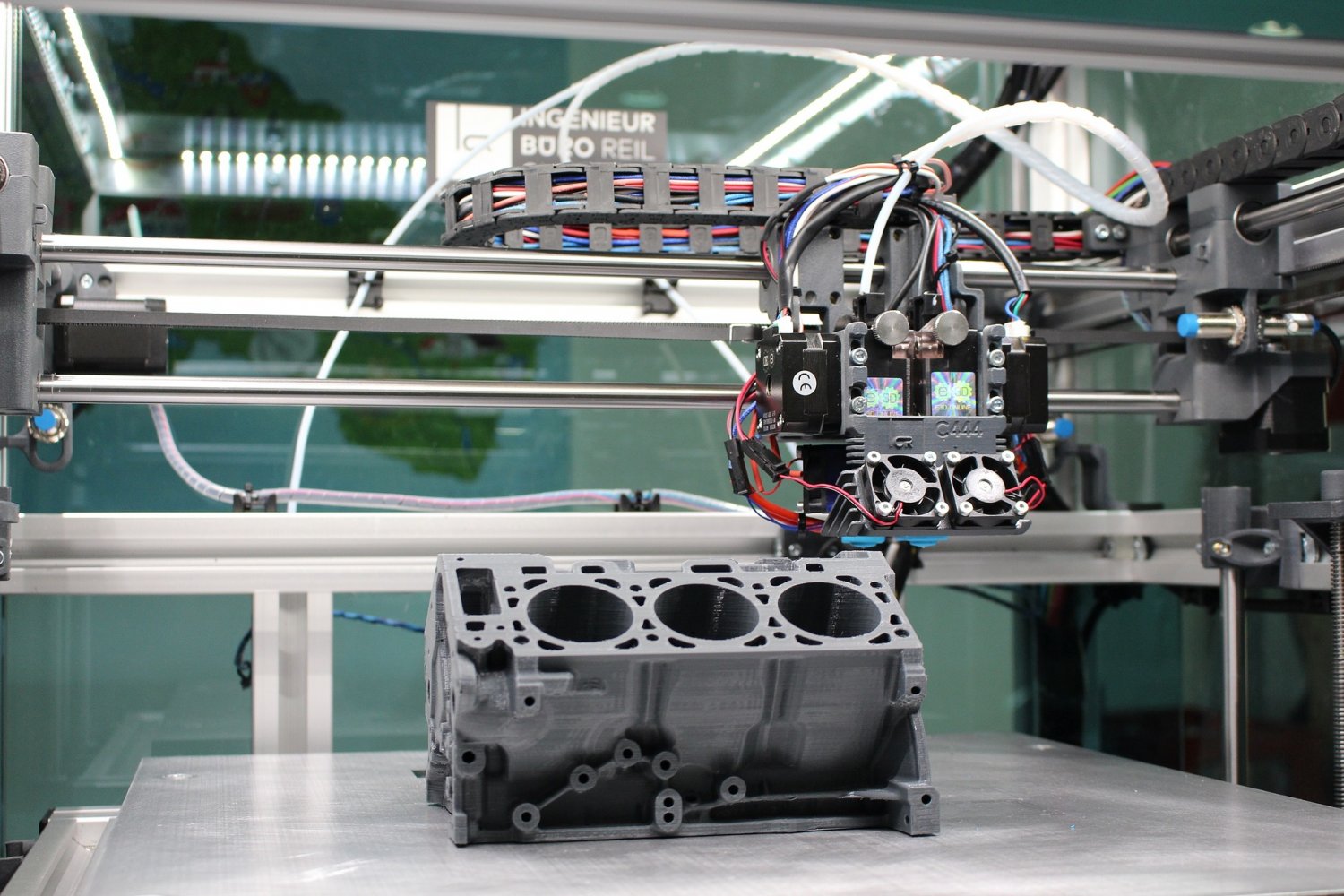
Aerospace and defense
Applications in additive manufacturing in the aerospace and defense sectors are currently focusing in enhancing the performance and efficiency of the vessels (weight reduction) and the decrease in enviromental polution and noise. Due to the special characteristics of aerospace components, usually complex and fabricated in short series, the introduction of this technique represents a disruption that will change the way in which future aircrafts are designed and constructed.
Automotive industry
This industry is an advanced prototyping user, so the adoption of additive manufacturing has been somehow easy, in such a way that it is currently being utilised for the obtention of functional prototypes, substitution pieces in old cars and complex parts for luxury models.
Electronics
This sector covers different fields like computers, mobile telephones, circuits and radio transmitter systems. Due to the miniaturisation and the importance of integrating functions in different structures, the manufacturing of integrated electronic systems and circuits represents one of the most exciting applications in the field of AM.
Construction
Building prefabricated houses is one of the fields which has generated more interest in the construction field in the last decade. The application of AM techniques will allow saving materials and transport costs, with the construction taking place in the same location where the house will be installed. Another advantages of AM in the building sector include fixing obsolete pieces, development of complex architectural designs, waste reduction and reutilisation in a more environmentally-friendly way.
Energy
Several opportunities exist nowadays for the application of AM in processes and materials related to energy. We can highlight the possibility to obtain prototypes in a fast way to reduce costs and delivering time in the development of novel products with improved energy efficiency and/or density. For example, the design of enhanced fuel cells is one of the fields withinthe energy sector where AM is currently being used widely.
Biomedical sector
Th use of AM techniques in modern biomedicine is one of the fields which has grown most in recent years and with the highest expansion potential, with a big demand coming from end users. With this method unique pieces and implants adapted to each user can be obtained, with a precision difficult to obtain by traditional methods that normally represent a very high cost. Customization linked to the development of matrices and biocompatible systems for tissue and 3D models, are only some of the action fields for AM in the biomedical sector.
CONTACT ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING AND COMPONENTS DIVISION:
Telephone: (+34) 987 440 481
E-mail: additive.manufacturing(at)icamcyl.com